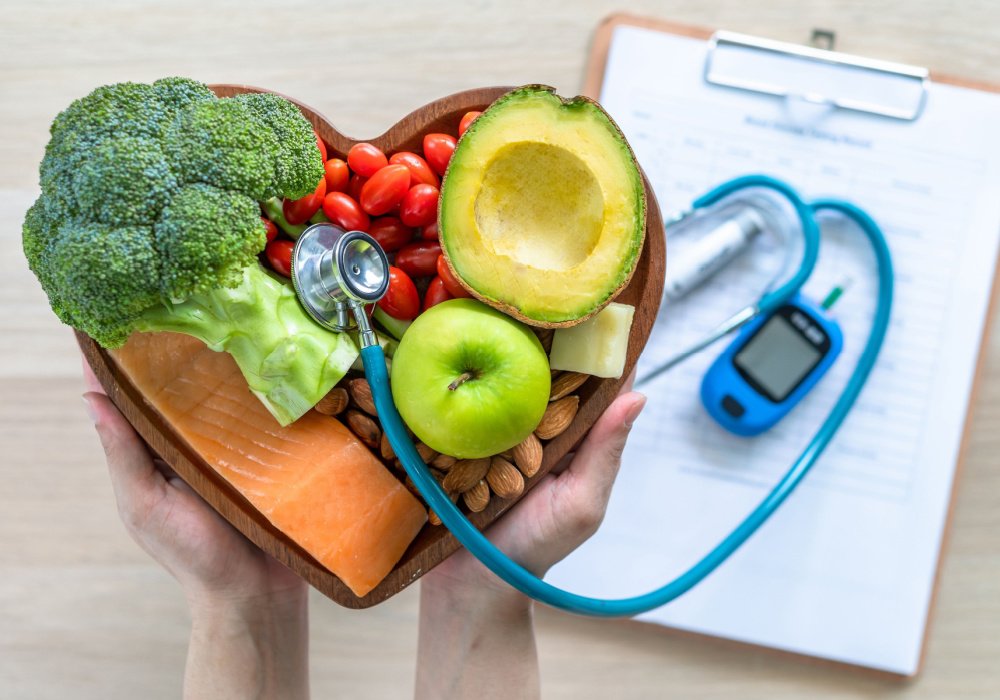
Managing diabetes effectively requires a keen understanding of the foods we consume. Reading nutrition labels is essential for individuals with diabetes to make informed dietary choices. These labels provide critical information that can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and overall health. In this article, we will explore how to read nutrition labels specifically for diabetes management. We will also discuss important nutrients, practical tips, and frequently asked questions.
Understanding Nutrition Labels for Diabetes Management
Nutrition labels are found on most packaged foods and beverages. They provide crucial information about the product’s nutritional content. Key components include serving size, calories, macronutrients, vitamins, and minerals. For individuals managing diabetes, understanding these components is vital.
Essential Components of Nutrition Labels for Diabetes Management

- Serving Size: This indicates how much food is considered one serving. All nutritional information on the label is based on this amount. If you eat more than the listed serving size, adjust the nutritional values accordingly.
- Calories: Total calories show how much energy you will obtain from the food. Monitoring calorie intake is important for maintaining a healthy weight. This can help manage diabetes effectively.
- Total Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates impact blood sugar levels directly. The total carbohydrates listed include sugars, starches, and fiber. It is essential to monitor carbohydrate intake to prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Sugars: This section breaks down total carbohydrates into natural sugars and added sugars. Limiting added sugars is crucial, as they can lead to rapid increases in blood sugar levels.
- Fiber: Dietary fiber is important for digestive health. It can also help regulate blood sugar levels. Foods high in fiber slow down the absorption of sugar, leading to more stable blood sugar levels. Aim for products with at least 3 grams of fiber per serving.
- Protein: Protein maintains muscle mass and promotes satiety. Including adequate protein in your diet can help you feel fuller for longer. This reduces the likelihood of snacking on high-carb foods.
- Fats: Pay attention to total fat content, as well as saturated and trans fats. Opt for products low in these unhealthy fats, as they can lead to heart disease, a risk for individuals with diabetes.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Look for products rich in essential vitamins and minerals. These contribute to overall health. Nutrients like magnesium, chromium, and zinc can play a role in blood sugar regulation.
The Importance of Portion Control in Diabetes Management
Portion control is equally important as understanding nutrition labels. The serving size indicated on the label can often be misleading. It may not reflect how much you typically consume. To manage your blood sugar effectively, consider using measuring cups or a food scale. This will ensure you are eating appropriate portion sizes.
Practical Tips for Reading Nutrition Labels in Diabetes Management
- Familiarize Yourself with Common Ingredients: Learn to recognize ingredients that spike blood sugar levels. High fructose corn syrup, white flour, and unhealthy fats are common culprits.
- Focus on Whole Foods for Better Diabetes Management: Choose whole foods with minimal processing. They typically have fewer added sugars and unhealthy fats. Fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats should form the foundation of your diet.
- Use the 5/20 Rule for Diabetes Management: This rule helps you assess whether a food is high or low in specific nutrients. If a nutrient is 5% or less of the Daily Value (DV), it’s low; 20% or more is high. This helps you make better choices regarding fiber, sugar, and fat content.
- Be Cautious with “Healthy” Claims: Just because a product is labeled as “sugar-free,” “low-fat,” or “gluten-free” doesn’t mean it is healthy. Always check the nutrition label for overall nutritional content.
- Look for Added Sugar Content: Aim for products with no more than 5 grams of added sugar per serving. Remember that sugar can be listed under different names, such as cane sugar or corn syrup.
- Keep a Food Diary for Effective Diabetes Management: Tracking your food intake helps you understand how different foods affect your blood sugar levels. Use a notebook or an app to log your meals, snacks, and blood sugar readings.
Frequently Asked Questions About Diabetes Management
1. How often should I check nutrition labels for diabetes management?
You should check nutrition labels every time you buy packaged foods. This habit ensures you make informed choices based on your dietary needs.
2. Are there specific nutrients I should focus on for diabetes management?
Yes, focus on carbohydrates, added sugars, fiber, and healthy fats. These nutrients can significantly impact blood sugar levels.
3. Can I eat processed foods if I have diabetes?
Yes, but it is essential to choose healthier options and read nutrition labels carefully. This helps avoid excess sugars and unhealthy fats.
4. How can I incorporate more fiber into my diet for diabetes management?
You can increase fiber intake by consuming whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables. Aim for at least 25 grams of fiber per day.
5. What are some low-sugar alternatives I can use?
Consider using natural sweeteners like stevia or monk fruit. Additionally, choose unsweetened products whenever possible.
Conclusion
Reading nutrition labels is an essential skill for anyone managing diabetes. By understanding the various components, you can make informed decisions that positively impact your blood sugar levels and overall health. Focus on whole foods, practice portion control, and be mindful of added sugars and unhealthy fats. With practice and awareness, you can navigate the world of nutrition labels confidently.
Embrace this knowledge as a powerful tool in your journey toward better diabetes management and improved well-being. By mastering the art of reading nutrition labels, you can take charge of your health. Make choices that support your diabetes management goals. Remember, every small change adds up. With consistency, you can pave the way for a healthier future.